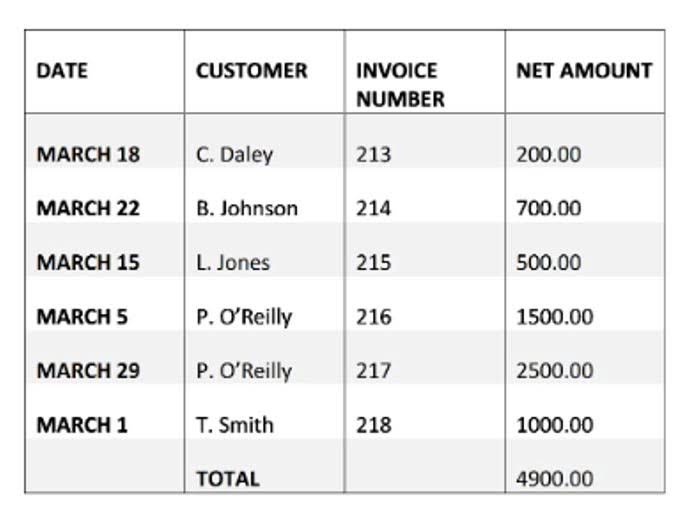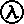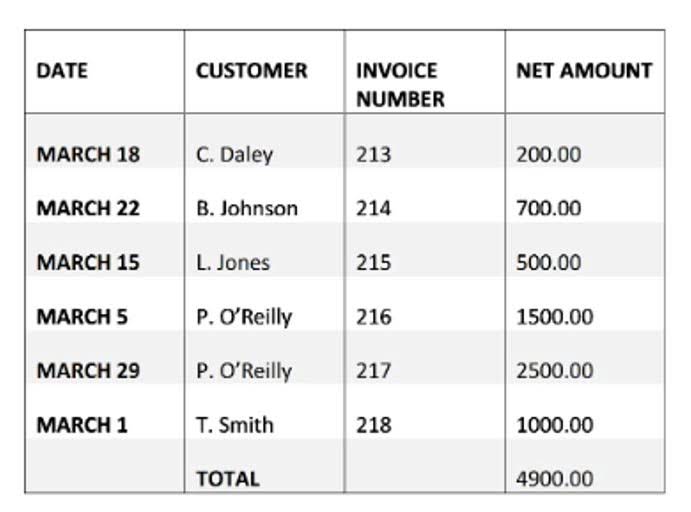
All such information realization of revenue definition accounting is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. As another example, consider that Mr. A sells goods worth $2,000 to Mr. B. The latter consents that the goods will be transferred after 15 days.
Intro to Revenue Recognition: GAAP Principles
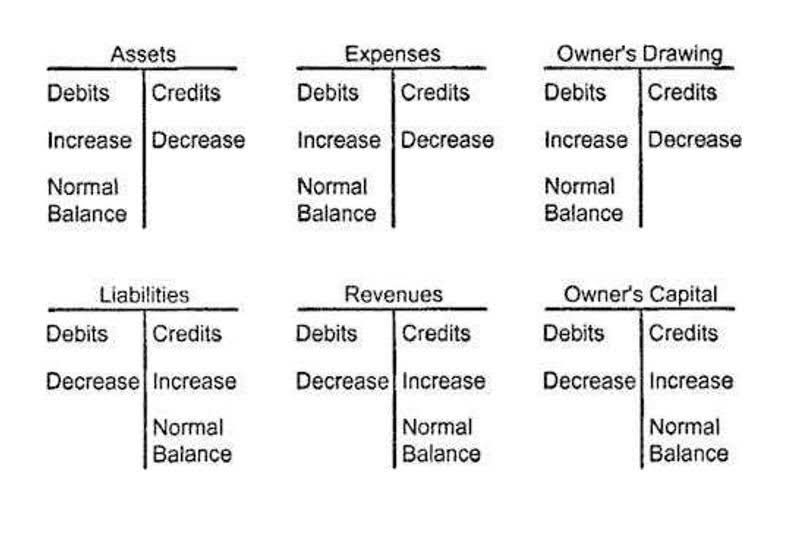
The revenue recognition principle of accounting (also known as the realization concept) guides us when to recognize revenue in accounting records. According to this concept, revenue should not be recognized by an entity until it is (i) earned and (ii) realized or realizable. Before exploring the concept further through examples, we would briefly explain these two conditions (i.e., earned and realized or realizable) imposed by the revenue recognition principle. Recognition of revenue on cash basis may not present a consistent basis for evaluating the performance of a company over several accounting periods due to the potential volatility in cash flows. Fortunately, revenue recognition automation services like RightRev exist to take this burden off your accounting team’s plate. With its powerful, scalable, and flexible solutions and products, RightRev can save your company from error-prone processes and wasted time sorting through contracts to ensure accurate and compliant GAAP revenue reporting.
- The performance obligations are the contractual promise to provide goods or services that are distinct either individually, in a bundle, or as a series over time.
- Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
- Unearned revenue is a liability that is subsequently converted to earned revenue when the related goods or services are provided to customers.
- Revenue recognition dictates when and how a company should record its revenue on its financial statements.
- Your revenue realization rate is the amount of revenue you actually recognized on fiancial statements compared to what you initially expected.
Related terms

The realization concept is that the revenue is recognized and recorded in the period in which they are realized; similarly to accrual basis accounting. In similar term, we realize as revenues when we deliver the agreed product with customers or the services have been rendered to them. The realization principle is a fundamental accounting concept that dictates when revenue should be recognized in the financial statements.

How does the realization Principles of Accounting affect income reported on a company’s balance sheet?
- To start, be careful not to recognize revenue too early, especially for long-term contracts, so you don’t mislead investors with your financials.
- Uncle Joe thinks your idea is so cool and places an order for 10 cups of lemonade even before you open shop.
- Some events are very obvious for example exchanging cash for a product or service.
- These methods can significantly impact financial reporting and when income is recognized on a company’s financial statements.
- Public companies in the U.S. must abide by generally accepted accounting principles, which sets out principles for revenue recognition.
Any receipts from the customer in excess or short of the revenue recognized in accordance with the stage of completion are accounted for as prepaid income or accrued income as appropriate. On the other hand, recognizing revenue at the point of delivery means that revenue is recognized only when the product or service is delivered to the customer, ensuring the company has fulfilled its obligation. An example is Peloton recognizing revenue when its purchased product (the Peloton bike) reaches the customer’s doorstep. Over time, revenue recognition standards have evolved to meet changing business practices and technological advances.

Meanwhile, construction companies usually recognize revenue over time as a project progresses, based on the percentage of completion method, rather than recognizing it all at once after completing the project. This method considers costs incurred and efforts expended as a proportion of the total project costs to determine when and how much revenue can be recognized. Accounting teams must follow the revenue recognition principle per GAAP when recording revenue. Below, we explore the implications of these principles on a company’s financial statements and business strategies. Certain businesses must abide by regulations when it comes to the way they account for and report their revenue streams.
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report.
- This principle helps public and private companies align their accounting practices with the revenue recognition principle to achieve accurate financial reporting.
- It is a cornerstone of accrual accounting together with the matching principle.
- The company is reasonably certain that the payment against the same will be received from the customer.
- In addition, ASC 606 shifted revenue recognition away from a very rules-heavy orientation to one that is more judgment-based—giving companies the chance to provide context and reasoning behind their financial picture.
- If a customer purchases a one-year subscription for $1,200, the company would recognize $100 in revenue each month, reflecting the delivery of services over time.
- The revenue realization principle is based on the revenue recognition principle — that is, that revenue is only recognized when it has been earned, regardless of whether payment has been received or not.
Understanding and applying the appropriate revenue recognition criteria is essential for ensuring transparency and maintaining the integrity of financial statements. However, making these determinations quickly becomes much more complicated when a company sells and delivers the goods or services at a later date or over time. In case of the rendering of services, revenue is recognized on the basis normal balance of stage of completion of the services specified in the contract.

In this case, under the realization principle, revenue is earned in May (i.e., when the transfer took place, notwithstanding the fact that the order was received in April and cash was received in June). In a business, it is important to differentiate between the events that actually happen in the business and the cash collected in the business. Events are good predictors of future cash flow but the occurrence of an event does not always correspond with the collection of cash.

 НОВОСТИ
НОВОСТИ Half-Life
Half-Life Half-Life 2
Half-Life 2