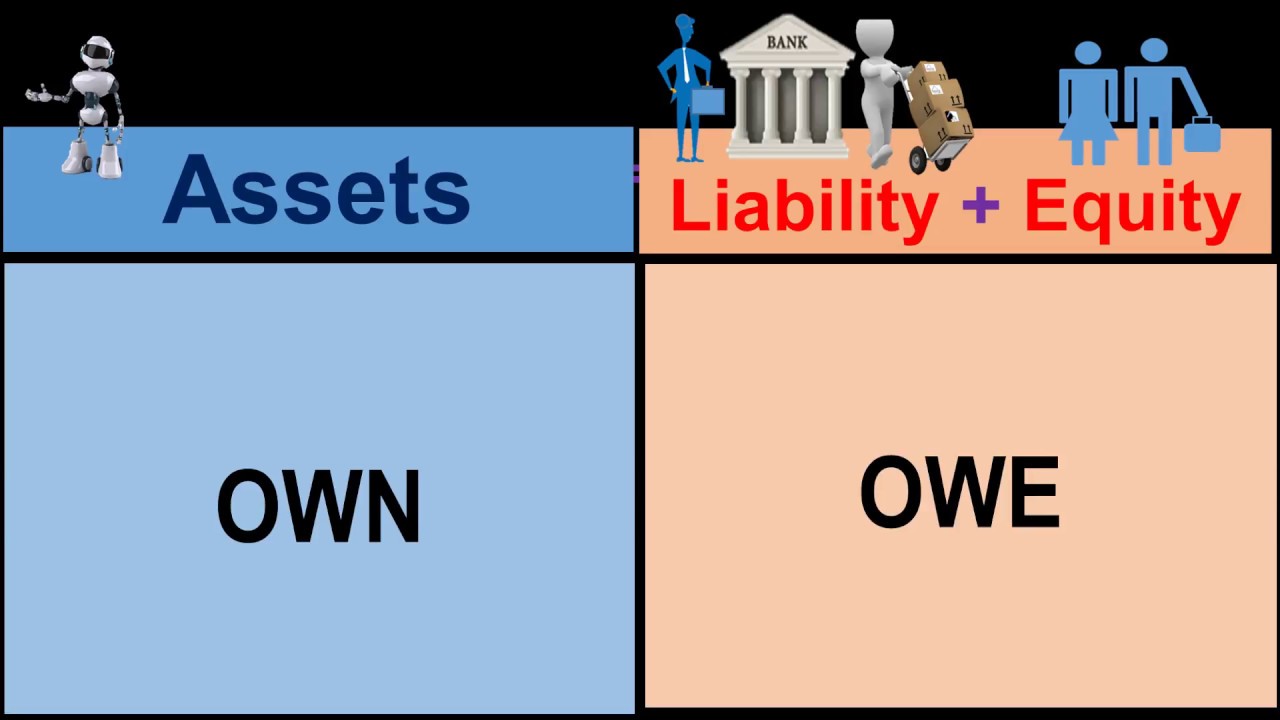
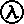If you were to take a clipboard and record everything you found in a company, you would end up with a list that looks remarkably like the left side of the balance sheet. A balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial performance at a given point in time. This financial statement is used both internally and externally to determine the so-called “book value” of the company, or its overall worth.
Balance Sheet: Explanation, Components, and Examples
- This number is the sum of total earnings that were not paid to shareholders as dividends.
- This transaction also generates a profit of $1,000 for Sam Enterprises, which would increase the owner’s equity element of the equation.
- During the month of February, Metro Corporation earned a total of $50,000 in revenue from clients who paid cash.
- Because there are two or more accounts affected by every transaction carried out by a company, the accounting system is referred to as double-entry accounting.
- The purpose of this article is to consider the fundamentals of the accounting equation and to demonstrate how it works when applied to various transactions.
The effect of this transaction on the accounting equation is the same as that of loss by fire that occurred on January 20. This transaction also generates a profit of $1,000 for Sam Enterprises, which would increase the owner’s equity element of the equation. On 10 January, Sam Enterprises sells merchandise for $10,000 cash and earns a profit of $1,000. As a result of this transaction, an asset (i.e., cash) increases by $10,000 while another asset ( i.e., merchandise) decreases by $9,000 (the original cost). On the other side of the equation, a liability (i.e., accounts payable) is created. On 2 January, Mr. Sam purchases a building for $50,000 for use in the business.
Balance Sheet Formula
The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. 11 Financial is a registered investment adviser located in Lufkin, Texas. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links.
Equity
The accounting equation is fundamental to the double-entry bookkeeping practice. Its applications in accountancy and economics are thus diverse. These are some simple examples, but even the most complicated transactions can be recorded in a similar way.
Expanded Accounting Equation: Definition, Formula, How It Works
As a result of the transaction, an asset in the form of merchandise increases, leading to an increase in the total assets. At this point, let’s consider another example and see how various transactions affect the amounts of the elements in the accounting equation. Capital essentially represents how much the owners have invested into the xero® a1 bow sight business along with any accumulated retained profits or losses. The capital would ultimately belong to you as the business owner. A bank statement is often used by parties outside of a company to gauge the company’s health. Last, a balance sheet is subject to several areas of professional judgement that may materially impact the report.
Who Prepares the Balance Sheet?
Since they own the company, this amount is intuitively based on the accounting equation—whatever assets are left over after the liabilities have been accounted for must be owned by the owners, by equity. These are listed at the bottom of the balance sheet because the owners are paid back after all liabilities have been paid. Under the accrual basis of accounting, expenses are matched with revenues on the income statement when the expenses expire or title has transferred to the buyer, rather than at the time when expenses are paid. The accounting method under which revenues are recognized on the income statement when they are earned (rather than when the cash is received). The balance sheet reports the assets, liabilities, and owner’s (stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time, such as December 31.
We also allow you to split your payment across 2 separate credit card transactions or send a payment link email to another person on your behalf. If splitting your payment into 2 transactions, a minimum payment of $350 is required for the first transaction. All programs require the completion of a brief online enrollment form before payment. If you are new to HBS Online, you will be required to set up an account before enrolling in the program of your choice. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. He is the sole author of all the materials on AccountingCoach.com.
The shareholders’ equity number is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities. The accounting equation helps to assess whether the business transactions carried out by the company are being accurately reflected in its books and accounts. This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is considered to be the foundation of the double-entry accounting system.
As noted above, you can find information about assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity on a company’s balance sheet. The assets should always equal the liabilities and shareholder equity. This means that the balance sheet should always balance, hence the name. If they don’t balance, there may be some problems, including incorrect or misplaced data, inventory or exchange rate errors, or miscalculations. In short, the balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of what a company owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by shareholders. Balance sheets can be used with other important financial statements to conduct fundamental analysis or calculate financial ratios.

 НОВОСТИ
НОВОСТИ Half-Life
Half-Life Half-Life 2
Half-Life 2